Drug efficacy and safety are significantly impacted by absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity, which are together referred to as ADMET. In the drug design process, predicting ADMET characteristics is crucial. ADMET prediction techniques are particularly useful during the lead optimization phase to help fix any persistent ADMET liabilities in the lead series.
Our company provides a specialized ADMET prediction service that accurately predicts ADMET properties using a wide range of computer models and a sizable pharmacological library. Our service aids researchers in removing compounds with subpar ADMET properties and greatly lowers R&D expenses.
Service Overview
Our company has a wealth of experience developing quantitative conformational relationships (QSAR), Free-Wilson models, and other models using project data or available data to forecast various ADMET properties of novel compounds and to help multi-parameter design process optimization. To estimate characteristics and forecast metabolic sites, we can also use well-established ADMET models from software companies and open source apps. Our ADMET forecasts offer details on dose frequency and size, including oral absorption, bioavailability, brain penetration, clearance, and distribution (frequency).
Service Contents
- pKa prediction, including all microstates.
- CYP metabolite production and kinetic parameters.
- Confidence estimation in classification models.
- Interactive distribution maps and 2-D and 3-D scatter plots.
- QSPR/QSAR model customization.
Research Capabilities
The computational approach to Our company's ADMET predictions requires consideration of two aspects, namely data modeling and molecular modeling.
Molecular modeling includes methods such as protein modeling, which uses quantum mechanical methods to assess the likelihood of interactions between small molecules and proteins known to be involved in the ADME process. Understanding the protein's three-dimensional (3D) structure is necessary for this. In the absence of a protein structure, we can create one by homology modeling the pertinent structure.
The PHAMACOPHORE model, which is based on the superposition of known substrates of the protein, can be used as a substitute technique to evaluate the interaction of small molecules with particular proteins in the absence of structural information about the protein.
Data modeling usually applies quantitative conformational relationship (QSAR) methods.
In addition, we have research capabilities in quantum mechanical (QM) simulations and molecular dynamics simulations. QM is a key approach to modeling protein structures and binding ligands. Molecular dynamics simulations play an important role in modeling ADMET-related proteins, such as exploring the protein conformation of flexible proteins or calculating energy using free energy perturbations (FEP).
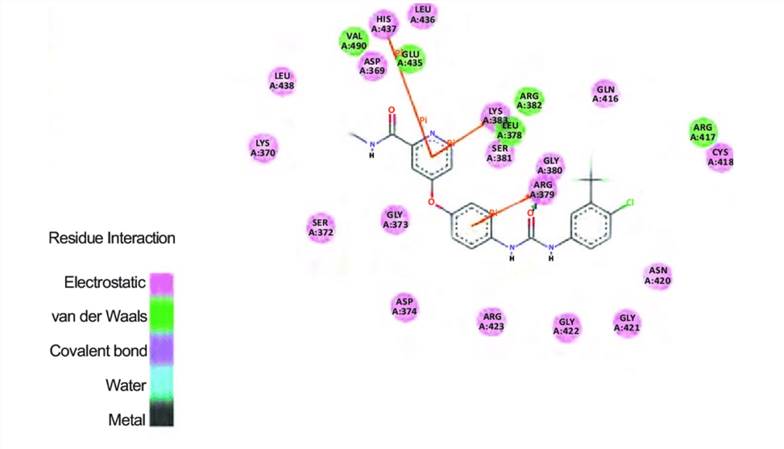 Fig.1 The ADMET prediction of both the best-docked compound Sorafenib. (Khandelwal R, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 The ADMET prediction of both the best-docked compound Sorafenib. (Khandelwal R, et al. 2018)
With the expanding understanding of protein structures, ADMET-related targets will become a very attractive area for computer-aided drug design in the near future. If you are looking for smarter, higher quality solutions that incorporate best practices, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Khandelwal R, et al. (2018). "Structure-based Virtual Screening for the Identification of High-affinity Small Molecule Towards STAT3 for the Clinical Treatment of Osteosarcoma." Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 18(29): 2511-2526.
Related Services
It should be noted that our service is only used for research, not for clinical use.

 Fig.1 The ADMET prediction of both the best-docked compound Sorafenib. (Khandelwal R, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 The ADMET prediction of both the best-docked compound Sorafenib. (Khandelwal R, et al. 2018)