Our company provides pesticide metabolism and toxicokinetic testing services in accordance with international quality system requirements. Our pesticide metabolism studies focus on elucidating the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of pesticides in experimental animals (including radioactive or non-radioactive studies), as well as the metabolic pathways, and to explore the kinetic laws.
It provides a scientific basis for further research on the toxic mechanism of action and toxic safety evaluation of the pesticide. In addition, we can also provide pesticide plant metabolism studies and pesticide animal metabolism studies.
Pesticide Metabolic Kinetic Test Overview
Our company offers this testing service to help clients study the following elements of the test sample:
- The route of entry into the organism, the rate and degree of absorption (bioavailability).
- Characteristics of distribution in the body among organs, tissues and body fluids, reversible binding to plasma proteins.
- Rate and degree of biotransformation, identification of the chemical structure of the main metabolites.
- Pathways, rate and capacity of elimination or excretion.
- Potential for, extent and duration of accumulation in the body;
- Comparison of the kinetic characteristics of absorption, distribution, biotransformation and elimination or excretion at different dose levels, single and multiple repeated dye hits.
- Compare the similarities and differences in toxicokinetics between different species and strains of animals to provide a possible basis for extrapolation to humans based on animal data.
Test Range
Organophosphorus insecticide, organophosphorus insecticide, diamide insecticide, neonicotinoid insecticide, carbamate pesticide, organic gas pesticide, benzoyl gland insecticide, pyrethroid pesticide, inorganic insecticide, biogenic insecticide, organic sulfur pesticide, pyrrole pesticide, fungicide, triazole fungicide, moringa fungicide, paclobutrazol, dimethoate, paraquat, quinclorac, isoxaflutole, gramophone, high-efficiency cover grass energy, plant growth regulator, etc.
Safety Evaluation Solutions
Our company uses the appropriate route to introduce the test sample into the experimental animal. Depending on the purpose of the study, a single dose of poison is selected or the dose is repeated several times over a defined period of time. The amount or concentration of the sample and/or its metabolites in body fluids, belly organs, tissues, and excreta is then measured over time, as required by the study.
Then, appropriate models and mathematical expressions are selected to derive the relevant toxicokinetic parameters and explore their toxicological significance. The specific study depends on the purpose of the study and the type, use, physicochemical properties, toxicity and toxicological characteristics of the sample.
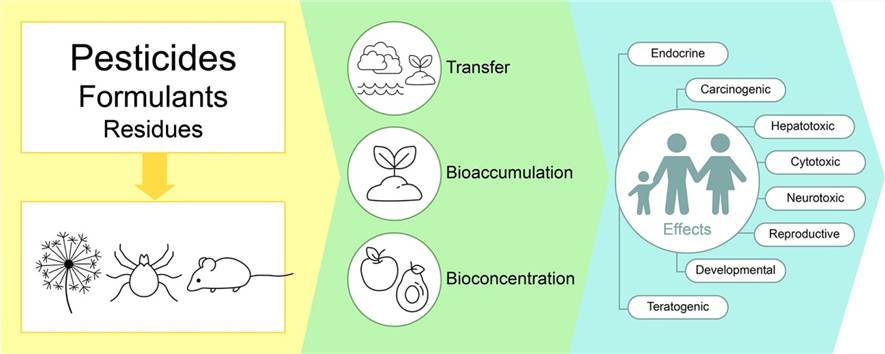 Fig.1 Pesticide residues can have long-term negative effects on human and animal health as well as on the stability of ecosystems. (Kalyabina V, et al. 2021)
Fig.1 Pesticide residues can have long-term negative effects on human and animal health as well as on the stability of ecosystems. (Kalyabina V, et al. 2021)
Test Samples
The purity of the test sample should not be less than 98%. If radioisotope-labeled samples are used, the radiochemical purity should not be less than 95%. If the impurity content is ≥ 20%, the type and content of impurities should be analyzed and identified.
To meet the needs of the dose of contamination, we can dissolve or evenly suspend the sample in an appropriate medium.
Test Animals
We use animal strains with similar metabolic pathways to humans whenever possible. The first adult rats are generally preferred, but other animals may be used upon request.
Route of Infection
Upon request, we can use oral or percutaneous inhalation. Intravenous injection is necessary to understand the basic toxicokinetic characteristics of the sample.
Observation Items
- Dynamic changes in the concentration of intravenously injected blood samples and analysis of basic toxicokinetic characteristics.
- Absorption analysis: absorption through the digestive tract, absorption through the skin, absorption through the respiratory tract
- Drug distribution analysis.
- Biotransformation analysis.
- Elimination and excretion analysis.
If you are looking for the best solution in the field of pesticide toxicology research, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Kalyabina V, et al. (2021). "Pesticides: Formulants, Distribution Pathways and Effects on Human Health - A Review." Toxicology Reports. 8: 1179-1192.
Related Solutions
It should be noted that our service is only used for research, not for clinical use.


 Fig.1 Pesticide residues can have long-term negative effects on human and animal health as well as on the stability of ecosystems. (Kalyabina V, et al. 2021)
Fig.1 Pesticide residues can have long-term negative effects on human and animal health as well as on the stability of ecosystems. (Kalyabina V, et al. 2021)