In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation assays are in vitro genetic toxicology tests that use cultured mammalian cells as indicator organisms. Our company offers professional in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation testing services for the detection of chemically induced mutations, including base pair mutations, shift mutations and deletions, to evaluate the potential for mutations in test samples.
Test Range
Veterinary drugs, pesticides, chemicals, fungicides, organic toxicants, solid waste, domestic waste leachate, hazardous waste, sewage, sludge, water quality, surfactants, etc.
About In vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Test Service
The following are available from Our company's in vitromammalian cell gene mutation testing service.
Test Cells
Commonly used cell lines include mouse lymphoma cells (L5178Y), Chinese hamster lung cells (V79), Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO), human lymphoblastoid cells (TK6), etc. The cells are examined for the presence of mycoplasma contamination before we used them.
Common genetic endpoints for these cell lines are the detection of thymidine kinase (TK), and hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) gene mutations.
Test Method
This test is a forward mutation test that detects both base substitution mutagens and code shift mutagens.
Cells are autolyzed in the test sample for a certain period of time with and without the addition of a metabolic activation system, and then the cells are passaged and cultured.
For example, cells with normal TK levels were sensitive to trifluorothymidine (TFT) and thus could not grow and divide in the culture medium, while mutant cells were not sensitive and could continue to divide and form colonies in the selective culture medium containing TFT.
Based on the number of mutant colonies, we will calculate the mutation frequency to evaluate the mutagenicity of the samples.
Sample Preparation
Solid samples should be dissolved or suspended in a suitable solvent and diluted to the appropriate concentration. Liquid samples can be used directly or diluted to the appropriate concentration. Samples should be ready to use before use.
The solvent must be non-mutagenic, not chemically react with the sample, and not affect cell survival and activity. The preferred choice is distilled water. For water-insoluble samples other solvents are available, dimethyl alum (DMSO) is preferred but should be used at a concentration no greater than 0.5%.
Control Group
- Positive controls: When a metabolic activation system is used, the positive control must be a substance that requires metabolic activation and is capable of causing mutations; 3-methylcholanthrene, N-nitroso-dimethylamine, etc. can be used. Without a metabolic activation system, positive controls such as ethyl methanesulphonate, ethylnitrosourea, etc. can be used. Other suitable positive controls can also be used.
- Negative controls: The negative control should be treated the same as the sample except that it does not contain the sample.
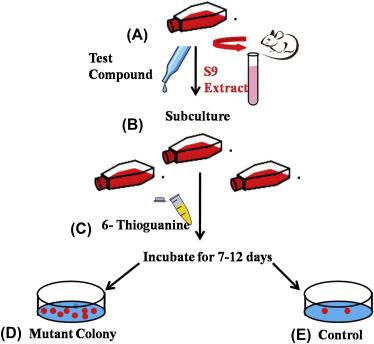 Fig.1 In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the Hprt and xprt genes. (Dixit M, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the Hprt and xprt genes. (Dixit M, et al. 2018)
In vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Test Report
The final test report Our company provides includes the following.
- Test name, test start and end dates, etc.
- Test summary.
- Sample: Name, identification information, CAS number (if known), purity, physical and chemical properties and stability of the test subjects related to this test, etc.
- Solvent and carrier: Basis for selection of solvent and carrier, solubility and stability of the sample in the solvent.
- Cell lines: Name, source, concentration and culture conditions (including the composition of culture medium, culture temperature, CO2 concentration and culture time).
- Test conditions: Dose, metabolic activation system, standard mutagen, and operating procedures.
- Test results: Means and standard deviations of toxicity and mutation frequencies of samples to cells in each dose group, whether there is a dose-response relationship, statistical results, means and standard deviations of simultaneous negative and positive controls, and historical ranges of negative and positive controls.
- Test conclusion: Whether the samples tested under the present test conditions are mutagenic.
For more information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Dixit M, et al. (2018). "In Vitro Gene Genotoxicity Test Methods." In Vitro Toxicology. 4: 67-89.
Related Solutions
It should be noted that our service is only used for research, not for clinical use.


 Fig.1 In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the Hprt and xprt genes. (Dixit M, et al. 2018)
Fig.1 In vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the Hprt and xprt genes. (Dixit M, et al. 2018)